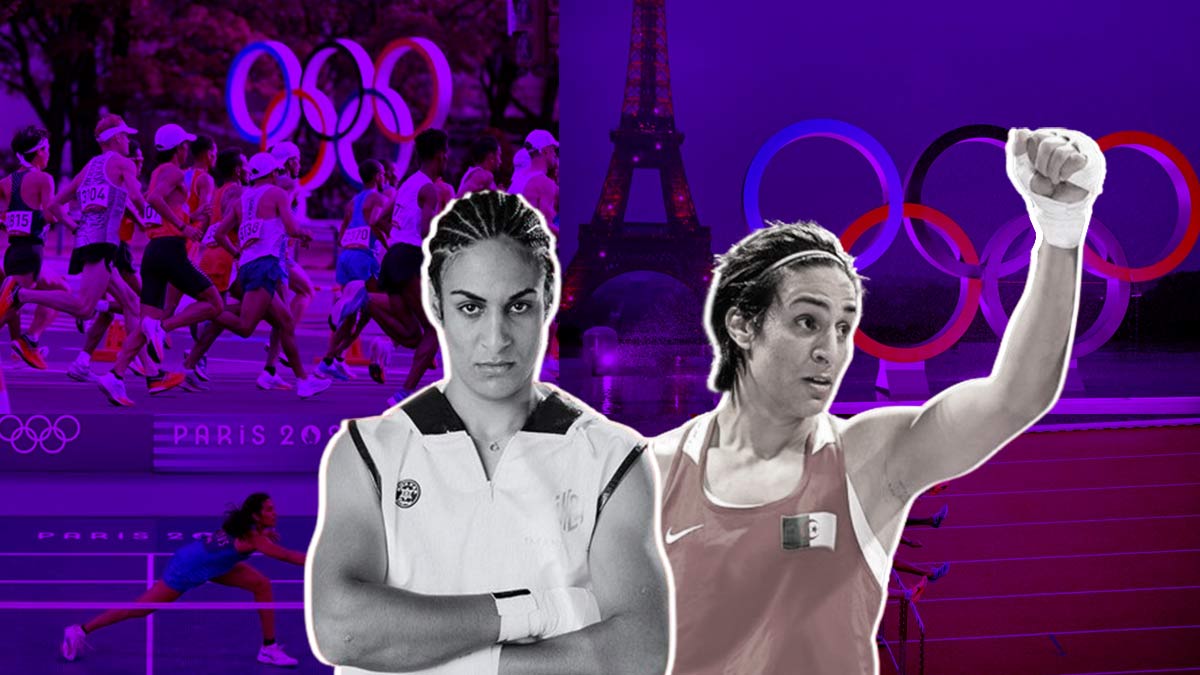
Algerian boxer Imane Khelif is at the centre of a gender eligibility controversy following her victory over Italian fighter Angela Carini at the Paris Olympics on August 1, 2024. This is Khelif's second appearance at the Olympics, having first competed for Algeria at Tokyo Olympics in 2021.
Since then, she has faced ongoing controversy, which has intensified after her recent win. Numerous comments and news articles have labelled Khelif as a "biological man" and questioned her eligibility to compete in women's boxing. A video of Khelif from 2022 has been widely shared on X, claiming she is "cheating in the Olympics," and has garnered millions of views.
Taiwanese boxer Lin Yu-Ting has also been drawn into the controversy. While much of the discussion has labelled both athletes as 'transgender,' there is no evidence or public statements confirming that either identifies as transgender. Both Khelif and Lin Yu-Ting have competed as women throughout their careers.
Everything was proceeding smoothly until the 2023 World Cup, organised by the International Boxing Association (IBA). The Russia-led IBA, which is not recognised by the International Olympic Committee (IOC), disqualified Imane Khelif after a gender eligibility test reportedly revealed she has XY chromosomes. IBA president Umar Kremlev has claimed that both Khelif and Taiwanese boxer Lin Yu-Ting, who allegedly had a similar test result, “were trying to deceive their colleagues and pretend to be women.” Khelif has denied these allegations.

Despite this, both Khelif and Lin Yu-Ting were admitted to the Olympic boxing competitions. The Boxing Unit, responsible for overseeing eligibility, ensured that all athletes met the required rules and medical regulations, including submitting verified medical certificates at least three months before the competitions.
IOC spokesperson Mark Adams defended the athletes at a news conference, stating, “These boxers are completely eligible. They are women on their passports, they have competed in the Tokyo Olympics, and have been competing for many years. We should avoid turning this into a witch hunt.”
Gender eligibility in sports has become a contentious issue, especially since the Tokyo Olympics. Some sports organisations have updated their rules to ban athletes who underwent male puberty from competing in women’s events. However, there is no evidence to suggest that either Khelif or Lin Yu-Ting experienced male puberty.
Don't Miss: 5 Trailblazing Women Making History At The Paris Olympics 2024
The IOC and the IBA adhere to different medical standards for athletes. The two organisations severed ties in 2019 when the IOC revoked the IBA’s Olympic status due to concerns about its integrity, finances, and governance. At the time, IBA president Gafur Rakhimov from Uzbekistan faced U.S. sanctions related to alleged involvement in drug trafficking and organised crime. Since the split, the IBA has been led by new president Umar Kremlev, who has accused Khelif and Lin of “deceiving their colleagues and pretending to be women.” However, the IBA no longer oversees the Olympic qualifying matches; the IOC manages these and has determined that Khelif and Lin meet the eligibility requirements.
The key point is that both Khelif and Lin are women who comply with the IOC's criteria for competing in the women’s category. There is no valid reason to bar them from competing. However, several media houses and critics of transgender inclusion in sports have seized upon the IBA's disqualification to label Khelif and Lin as engaging in gender fraud, accusing them of trying to unfairly secure Olympic medals.
Recent controversies have taken serious issues like hyperandrogynism, where female bodies produce excessive testosterone, and intersexuality, where individuals have sex characteristics that don't align neatly with traditional male or female definitions and used them to fuel an already heated debate over transgender women’s participation in sports.
Don't Miss: The God On Olympic Medals: What Does This Image Mean?
This situation echoes past controversies. For example, ace sprinter Dutee Chand was barred from competing as a female due to her condition, hyperandrogenism, which results in naturally high testosterone levels. The International Association of Athletics Federations (IAAF) required her to lower her testosterone levels through medication or surgery to compete as a woman. After being dropped from the 2014 Commonwealth Games, Chand won her case at the Court of Arbitration for Sport (CAS) and was later allowed to race again, bringing national pride through her achievements.

Similarly, Caster Semenya, a two-time Olympic champion and three-time world champion in the 800m, faced similar issues. Despite dominating her sport, her 2009 World Championships victory came under scrutiny after athletics' governing body requested a gender test. In 2018, World Athletics introduced new rules limiting testosterone levels for female runners in distances from 400m to the mile. Semenya, whose condition is 46 XY 5-ARD (5-alpha-reductase deficiency), could not compete without reducing her testosterone levels and lost her appeal at CAS in a landmark case in 2019.
Later Caster Semenya achieved a significant legal victory when the European Court of Human Rights ruled that she was discriminated against by track and field regulations requiring her to medically lower her natural hormone levels to compete, as per AP News. However, despite this success following her failed appeals in 2019 and 2020, the ruling did not overturn the controversial testosterone regulations, which the world track and field body confirmed would remain in effect.
We got in touch with Dr Pooja Mehta, Director - Unit Head Department of Obstetrics & Gynaecology, Marengo Asia Hospital, Gurugram who told us what is Hyperandrogenism and its impact on female athletes.
She told us “A disorder known as hyperandrogenism is defined by high amounts of androgens, or male hormones like testosterone, in people who are normally assigned to the female gender at birth. Numerous medical symptoms, such as hirsutism (excessive hair growth), acne, and irregular menstruation periods, can result from these high androgen levels.”
She further told us, “Athletes who have hyperandrogenism may also face serious social and psychological difficulties. Their mental health and self-esteem may suffer as a result of the stigma and scrutiny associated with the disease. Furthermore, treating the illness frequently calls for medical procedures that have potential negative consequences on general health and function in addition to their own set of side effects.”
When asked if it is fair to question a female athlete's gender due to hyperandrogenism, Dr Pooja said, “It's critical to understand that hyperandrogenism does not determine an athlete's gender on its own. Gender identity is a very personal experience that is not exclusively based on biological characteristics. Furthermore, it can be detrimental and discriminatory to question an athlete's gender based on their hormone levels. This can perpetuate stigma and have an impact on the mental health of athletes.”
She emphasised how medical justice should not be about labelling athletes as male or female based on hormone measurements, but rather about giving them the same chances and support.
Ultimately, despite the controversy and public scrutiny, Imane Khelif has consistently identified as a woman, and the IOC has permitted her to compete in the Olympics as such. In light of this, the matter should be considered settled.
Keep reading Herzindagi for more such stories.
Credits: Instagram
Also watch this video
Herzindagi video
Our aim is to provide accurate, safe and expert verified information through our articles and social media handles. The remedies, advice and tips mentioned here are for general information only. Please consult your expert before trying any kind of health, beauty, life hacks or astrology related tips. For any feedback or complaint, contact us at [email protected].